5 Causes of Diarrhea After Eating Fatty Foods & Tips for Treatment
Our content is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice by your doctor. Use for informational purposes only.
Experiencing diarrhea after indulging in fatty foods can be quite a discomfort. This condition can be attributed to various factors, ranging from simple issues like an exaggerated gastrocolic reflex and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) to more complex problems involving the gallbladder, pancreas, or bile acid malabsorption.
In this article, we’ll delve into each of these conditions, providing insights on identifying and managing them.
Key Facts:
- An exaggerated gastrocolic reflex is the most common cause of diarrhea after eating fatty foods.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) can also lead to diarrhea after consuming fatty foods.
- Gallbladder removal can cause diarrhea in up to 20% of patients.
- Bile acid diarrhea or fat intolerance can result in diarrhea after eating fatty foods.
- Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (EPI) or chronic pancreatitis can lead to maldigestion and problems such as diarrhea after eating fatty foods.
The table below summarizes the causes of diarrhea after fatty foods, with the following considerations:
- Most cases are either due to exaggerated gastro-colic reflex Or irritable bowel syndrome.
- Note that those are the causes of CHRONIC OR RECURRENT diarrhea after eating fatty foods.
- Always consult your doctor if you experience one of the red signs enlisted below.
| Diarrhea after eating fatty food causes | How to suspect (symptoms)? And how to deal. (Read the full article for a better understanding) |
1- Exaggerated Gastro-colic reflex: due to
|
|
| 2- irritable bowel syndrome |
|
| 3- removal of your gallbladder |
|
| 4- Bile acid diarrhea (Malabsorption) |
|
| 5- Exocrine Pancreatic insufficiency (EPI)/chronic pancreatitis. |
|
| *When to see a doctor. |
See a doctor IF you have any:
|
1- Exaggerated Gastro-Colic Reflex: The Usual Suspect
The gastro-colic reflex is a natural physiological process. When your stomach receives food, it signals your colon to increase its motility, resulting in an urge to defecate immediately after eating. This reflex can be exaggerated by eating large meals, consuming fatty foods, drinking a large amount of cold liquid, and experiencing stress and anxiety.
More exaggeration of the reflex can lead to diseases such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and Idiopathic dumbing syndrome (DS) (reference). Fats are one strong trigger of the gastrocolic reflex. An attack or two of diarrhea after fatty foods without other significant symptoms may reflect an abnormally strong gastrocolic reflex. As a gastroenterologist, I’m frequently being asked: I always poop immediately after eating, and I may have an attack or two of diarrhea. Most of the time, the cause is an exaggerated gastrocolic reflex without a specific gut disease.
Recognizing an Exaggerated Gastro-Colic Reflex:
- You feel the urge to defecate immediately after eating, especially after consuming fatty foods, large meals, or during stressful periods.
- Diarrhea occurs only after eating, not during fasting.
- Mild cramps or discomfort may be experienced after eating, which usually subsides after defecation.
- The diarrhea is typically yellow in color and greasy.
- There are no severe or persistent colics.
- There is no history of gallbladder removal or problems.
Managing an Exaggerated Gastro-Colic Reflex:
- Limit your intake of healthy fats and avoid unhealthy fats.
- Avoid large meals and excessive consumption of liquids at once.
- If the condition persists, consult your doctor to rule out similar conditions like IBS and bile acid diarrhea.
Learn more about Gastro-colic reflex and diarrhea after eating fatty foods:
Wikipedia: Gastrocolic reflex.
Verywellheath: your gastrocolic reflex with IBS.
2- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A Common Culprit
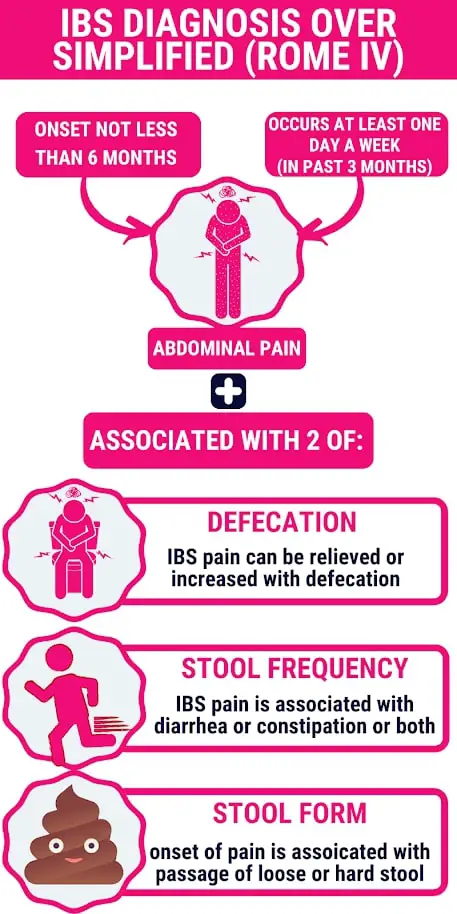
IBS is a chronic functional syndrome that affects the gut. It’s a common condition that affects approximately 10-15% of the population. If you experience diarrhea after eating fatty foods, it could be due to undiagnosed IBS.
Identifying IBS as the Cause:
- Abdominal pain or cramps are a key feature of IBS.
- The pain is recurrent and associated with defecation, changes in stool consistency, or stool frequency.
- Diarrhea after eating fatty meals is more commonly associated with the IBS-Diarrhea subtype.
- The condition may worsen with stress and anxiety.
- The diarrhea is not restricted to fatty foods and may be triggered by various foods such as FODMAPs and lactose.
Managing IBS:
- If you suspect you have IBS, consult your doctor.
- If you already have IBS, you can manage postprandial diarrhea by avoiding heavy meals, fatty meals, caffeine, lactose, FODMAPs, and managing your stress and anxiety.
- Over-the-counter medications for IBS pain relief and diarrhea may be helpful.
- Consult your doctor if there is no improvement.
3- Gallbladder Removal: A Potential Cause
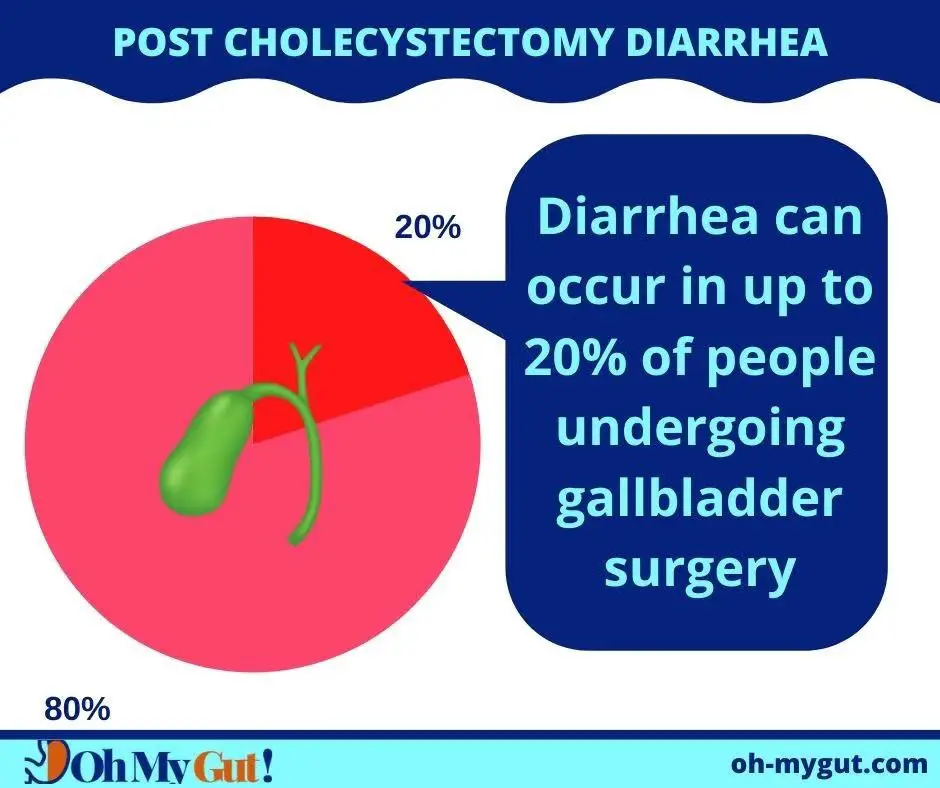
Diarrhea can occur in up to 20% of people who have undergone gallbladder surgery. This is usually mild and occurs after meals, but it may persist for years in some patients.
Identifying Gallbladder Removal as the Cause:
- You have a history of gallbladder removal and diarrhea onset after the surgery.
- Diarrhea may start before surgery during the cholecystitis stage and not resolve after surgery.
- Other symptoms include stomach cramps, gas, and bloating.
- Diarrhea can occur occasionally after eating fatty foods or become continuous and may be yellow.
Managing Post-Gallbladder Removal Diarrhea:
- Eating smaller meals and reducing dietary fat might help.
- Consult your doctor about medications that may relieve diarrhea, such as Imodium (loperamide) or cholestyramine.
4- Bile Acid Diarrhea / Fat Intolerance: A Less Common Cause
Bile acid malabsorption or bile acid diarrhea refers to diarrhea caused by the digestive system’s abnormal processing of bile acids. This condition is more common than you might think (reference).
Identifying Bile Acid Diarrhea:
- Diarrhea, usually of a yellow color, occurs after eating fatty foods or even at any time (not only after meals).
- Severe urgency and the risk of stool leakage may occur, especially in older ages.
- It is usually watery diarrhea, more frequent in obese people.
- Bloating and indigestion may be present.
Managing Bile Acid Diarrhea:
- Diagnosing bile acid diarrhea may be quite difficult for you and your doctor.
- If you always have diarrhea with an intense urgency, inform your doctor.
- Some doctors may request special tests or endoscopy; others may run a therapeutic test by treating you.
- The best treatment is a drug that binds to the bile acid inside the intestine and prevents its adverse effects, such as cholestyramine (Questran).
- Decrease the consumption of fatty foods. Opt for healthier fats present in avocados, fatty fish, and nuts.
Learn more about Excess Bile Production Symptoms and Causes.
5- Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (EPI)/Chronic Pancreatitis: A Rare Cause
Your pancreas secretes enzymes that digest food. When your pancreas is compromised, it will not secrete sufficient amounts of these enzymes, leading to maldigestion and problems such as diarrhea after eating fatty foods (reference).
Identifying EPI/Chronic Pancreatitis:
- Mild diseases may have no symptoms at all, or they may have mild symptoms such as abdominal discomfort and mild diarrhea after eating fatty foods, carbohydrates, or proteins.
- Moderate to severe disease: Maldigestion and diarrhea after eating fatty foods, carbohydrates, and proteins.
- Fatty diarrhea with loose greasy stool occurs in severe cases with more than 90% of pancreatic function loss.
- Bloating, flatulence, stomach cramps, and weight loss.
- Other symptoms of chronic pancreatitis, such as recurrent mid-epigastric pain, may be present.
Managing EPI/Chronic Pancreatitis:
- The condition is not common, but if you are an alcoholic and have symptoms consistent with the above list, consult your doctor.
- Your doctor may diagnose pancreatic insufficiency if you have troublesome chronic abdominal pain, greasy diarrhea, bloating, or a history of pancreatitis.
- After confirming the condition, the main treatment is replaced with an external pancreatic enzyme supplement.
- Mild symptoms may pass undiagnosed, but you may benefit from controlling the number of fatty foods to stop occasional mild diarrhea after eating fatty foods.
Learn more about pancreatic insufficiency: source1, source2
When to Seek Medical Attention
While diarrhea after eating fatty foods is often due to an exaggerated gastrocolic reflex or IBS, other less common medical conditions may cause the same postprandial diarrhea. Consult your doctor if diarrhea after eating fatty foods is associated with severe urgency or explosive diarrhea, soiling accidents, weight loss, fever, vomiting, continuous diarrhea after gallbladder removal, consistent greasy stool, symptoms consistent with IBS, or bloody diarrhea.
Remember, your health is paramount. Don’t hesitate to seek medical advice when you need it.
FAQs about diarrhea after eating fatty foods:
Can the gallbladder cause diarrhea right after eating?
Yes, the gallbladder plays a crucial role in digesting fats. It stores bile, a liver-produced substance that helps break down dietary fats. Suppose the gallbladder is removed or not functioning properly. In that case, the release of bile can be disrupted, leading to poor digestion of fats and potentially causing diarrhea soon after eating fatty foods.
What causes vomiting and diarrhea after eating fatty foods?
Several conditions can cause vomiting and diarrhea after eating fatty foods. These include gastroenteritis, food poisoning, gallbladder disease, or a severe form of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Sometimes, it could be a sign of food intolerance or allergy. If these symptoms persist, it’s important to seek medical attention.
What causes diarrhea a day after eating fatty foods?
Diarrhea, a day after eating fatty foods, could be due to various reasons. It could be a sign of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), gallbladder disease, or exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI). It could also be a symptom of bile acid malabsorption, where the body fails to properly reabsorb bile acids in the intestines, leading to watery stools.
How quickly can fatty or greasy food cause diarrhea?
The onset of diarrhea after eating fatty or greasy food can vary greatly depending on the individual and the underlying cause. For some, it can occur within a few hours of eating. This is often the case with conditions like an exaggerated gastrocolic reflex or IBS. For others, it might take a day or more, particularly if the cause is related to gallbladder disease or other digestive disorders. If you frequently experience diarrhea after eating fatty or greasy foods, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
- Evidence-based
- Written by a doctor.