Yellow diarrhea: 12 Causes, Doctor Explains.
Our content is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice by your doctor. Use for informational purposes only.
0- Yellow diarrhea: FAQ & Summary
Q1: What is the difference between yellow diarrhea and yellow stool?A: Yellow diarrhea is different from yellow stools. Yellow diarrhea doesn’t only mean your stool is yellow, but also it means that you have frequent loose or watery stools (diarrhea). Diarrhea means your poop is loose or watery Plus you have three or more loose stool motions per day. “Generally speaking, Any severe diarrhea can lead to yellowish stool because of diarrhea itself. As your poop passes quickly through your colon before it acquires its normal brown color”. |
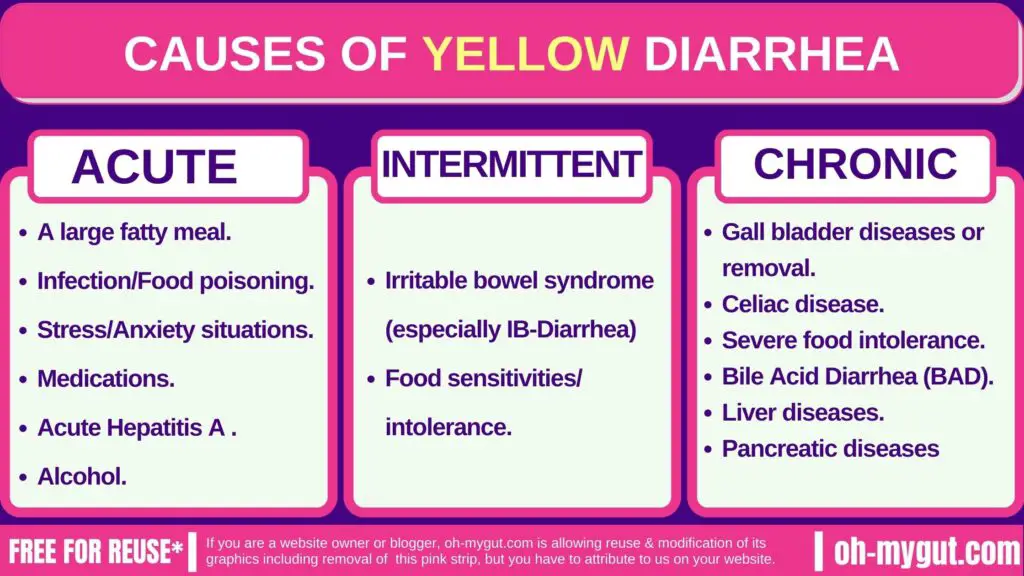
Q2: What are the most common causes of yellow diarrhea?A: Our favorite scheme for yellow diarrhea is the time frame in which diarrhea happened: 1- Acute yellow diarrhea: [attack for the first time, lasts from a day or a few days for a maximum of 14 days].
2- Recurrent Acute yellow diarrhea: [attacks for few days that comes and go for a long time, you are free between the attacks]
3- Chronic yellow diarrhea: [Usually lasts for months or Years]
|
Q3: Why is my diarrhea yellow? [mechanisms].A: Your stool Acquires its brown color for the breakdown of a substance called bilirubin inside your colon [secreted into your intestine through bile]. So, yellow diarrhea occurs due to either:
|
Q4: When to see a doctor for your yellow diarrhea?A: not all yellow diarrheas are dangerous. A single attack of yellow diarrhea lasts for a day or a few days and is usually not a cause of concern. But you have to see a doctor if Your yellow diarrhea is:
|
1- Causes of Acute Yellow Diarrhea:
A- Large Fatty Meals/ Indigestion:
Consuming an excessive amount of fat in one sitting can lead to difficulties in absorption. Consequently, undigested fat might end up in your stool, triggering a sudden bout of yellow diarrhea post the fatty indulgence. [ref]
Symptoms:
- Yellow diarrhea appearing shortly after a high-fat meal might be due to fatty foods.
- The stool can be oily, ranging from yellow to grey.
- Mild or absent abdominal discomfort.
- Potential nausea due to the high-fat presence in your stomach, but typically no vomiting.
- Duration ranges from a few hours up to 2 days, typically resolving on its own.
- NOT linked with high temperatures, intense abdominal pain, vomiting, mucus, or blood in the stool.
How to Manage:
- If you’re confident that your diarrhea is due to fatty foods, consider reducing your fat intake.
- Don’t eliminate fats entirely; consume them in moderation.
- Minimize consumption of unhealthy (saturated) fats such as:
- Fatty animal proteins.
- Highly processed foods.
- Opt for healthier (unsaturated) fat sources:
- Nuts and seeds.
- Fish and seafood.
- Olive oil.
- Avocado.
- Consult a physician if yellow diarrhea occurs even after consuming minimal fats. It might indicate other issues like bile acid diarrhea or problems with the gallbladder or pancreas.
Dive deeper with this article: Diarrhea after consuming fatty foods.
B- Acute Gastroenteritis/Food Poisoning:
Acute gastroenteritis is an inflammation of your digestive tract. It can lead to yellow diarrhea by accelerating the movement of colon contents or by affecting fat absorption, especially in cases of giardiasis.
Viruses, particularly Noroviruses, Rotavirus, and Astrovirus, are the primary culprits behind gastroenteritis. Bacterial infections are the next common cause. Parasites, especially giardiasis, can also result in yellow, foul-smelling, greasy diarrhea.
Symptoms:
- Diarrhea: Typically bright brown or yellow. Giardiasis might produce greasy, foul-smelling stools.
- Onset & Duration: Generally sudden, lasting between 1 to 4 days.
- Possible low-grade fever, though bacterial infections might cause higher temperatures.
- Presence of nausea and vomiting, though typically mild.
- Decreased appetite.
- Potential muscle soreness and headaches.
- Moderate to intense abdominal discomfort.
- Bloody stools or dysentery are typically NOT present.
MORE: 9 Causes of Lighter-Colored Poop & When to Worry.
How to deal?
Yellow diarrhea due to acute gastroenteritis (especially giardiasis) is usually a self-limiting condition within a few days. You have to:
- Drink more fluids.
- Eat frequent small meals and avoid heavy or fatty meals.
- Try to eat bland foods (BRAT): Bananas, Rice, Applesauce, and Toast.
- Try to avoid: fats, caffeine, sugary foods, dairy, and alcohol.
- See a doctor if: your diarrhea lasts for more than 3 days or if you have severe symptoms such as bloody stool, severe dehydration, intolerable abdominal pain, or persistent vomiting.
C- Stress/Anxiety-related diarrhea:
As with any type of diarrhea, speeding up your colon contents can lead to yellowish diarrhea. This speeding up is not due to infection or food intolerance all the time.
Yellow diarrhea may be simply due to anxiety or stressful situations such as exams, fears, or any stressful situations. This leads to fear response by your gut leading to attacks of yellow diarrhea [ref]
Stress/anxiety-related yellow diarrhea is different from Irritable bowel syndrome, as it occurs occasionally, is related to stressful conditions and it is not as frequent as irritable bowel syndrome symptoms.
It is a normal response from your body and you don’t have to be worried about it. Try to manage your anxiety condition and you will get rid of yellow diarrhea.
Avoid caffeine and alcohol as they may aggravate your yellow diarrhea with stress.
Only see a doctor if:
- Yellow diarrhea is frequent even with small stressors such as talking to strangers or with usually daily work stress.
- Diarrhea lasts a long time (days or weeks).
- Any abnormal symptoms such as fever, vomiting, intolerable abdominal pain.
Learn more: anxiety as a cause of yellow stool.
D- Alcohol drinking may also cause yellow diarrhea.
Yellow diarrhea may be simply due to faulty drinking habits. But it is worse to mention that in some persons, even small amounts of alcohol can cause yellow diarrhea. As alcohol irritates your digestive tract and speeds up things inside your intestines and colon [ref]
Another long-term problem with alcohol is that it can affect your liver and pancreas. Chronic liver diseases or chronic pancreatic insufficiency can lead to yellow diarrhea.
If your yellow diarrhea often starts after drinking ialcohol, especially with larger amounts, you have to stop it at all or restrict the amount you drink.
E- Some medications can cause Yellow diarrhea.
A good question to ask yourself is, is there any recent medication intake before the onset of your yellow diarrhea? More than 700 drugs are linked to diarrhea [ref]. Some of them are extremely common in households and over the counter.
Most commonly, Laxatives, antibiotics, metformin, and drugs are used to treat heartburn and gastritis.
1- Laxative overdose.
They include:
- Lactulose-containing laxatives.
- Docusate sodium.
- Magnesium Oral solutions and magnesium-containing laxatives.
They can cause yellow diarrhea if taken in large doses, as they can speed up your intestines or draw water from your blood into your colon.
Also, note that some Magnesium containing supplements that are not intended to be laxatives can cause yellow diarrhea as a side effect. Always check your medications for magnesium.
2- Antibiotics that can cause yellow diarrhea.
Many antibiotics can cause diarrhea as a side effect, and it can be:
- Mild self-limiting loose stool.
- Moderate to severe diarrhea that lasts for days (which is usually yellow diarrhea).
- Severe bloody diarrhea (severe colitis).
The most common antibiotics that can cause yellow diarrhea:
- Cephalosporins: such as ceftriaxone, cephalexin.
- Penicillins as amoxicillin and ampicillin.
- Clindamycin.
How to suspect antibiotic-associated diarrhea?
- If you have a recent history of taking antibiotics prior to the onset of yellow diarrhea.
- If you have a previous history of antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
- If you are taking more than one antibiotic at the same time, it will increase the odds of yellow diarrhea.
- Taking antibiotics for a long period (more than two weeks).
3- Recent Use of anti-Diabetes Mellitus drugs.
Some anti-diabetes drugs can lead to GIT disturbances and, consequently, yellow diarrhea. The most common medication to cause diarrhea is Metformin.
Metformin is a very common anti-diabetes medication that is widely prescribed by doctors. So if you have a recent history of metformin intake, consult your doctor about the medications.
And also not that Metformin can be present in combination with other anti-diabetes medications under different names. Always consult your doctor about your anti-diabetes medication if you experience gut problems or yellow diarrhea.
4- Gastritis & GERD yellow stool is usually due to medications.
If you have Gastritis or GERD, you may experience yellow diarrhea. This occurs mainly not because of GERD itself, But due to the medication you use.
These medications can decrease the acidity of your stomach. Decreased acidity can lead to the overgrowth of unwanted bacteria and organisms inside your intestine and colon. So, the chronic use of GERD and anti-ulcer medications can lead to yellow diarrhea.
Common GERD medications that cause yellow diarrhea include:
- Proton Pump Inhibitors: such as Esomeprazole (Nexium ®), Pantoprazole (Protonix ®), Omeprazole (Prilosec ®).
- H2 Blockers: such as Famotidine, Ranitidine (Zantac ®)
IMPORTANT NOTICE:
GERD and Yellow diarrhea are not solely attributed to medications. Another connection found between GERD and Yellow diarrhea is Psycnic stress, such as anxiety and depression [ref].
Usually, people with psychic stress or complaining from certain psychiatric diseases such as anxiety will have multiple functional GI diseases simultaneously, such as GERD, Chronic/recurrent diarrhea (maybe yellow), IBS, functional dyspepsia, and others.
5- Other Medications that can cause yellow diarrhea:
- Chemotherapy (anticancer medications).
- Immunosuppressive drugs: such as Mycophenolate. Immunosuppressives are used in people with auto-immune disorders such as systemic lupus, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura.
- For the complete list of medications that can cause yellow diarrhea, click HERE and HERE.
F- Acute Hepatitis A [Yellow diarrhea + Jaundice].
Another cause of yellow diarrhea is the hepatitis A virus infection. It is a relatively common infection in third-world countries, especially among children [ref].
Hepatitis A usually causes yellow diarrhea, but it has a more distinctive feature which is jaundice (yellowish discoloration of skin and sclera).
It is acquired via the fecal-oral route by ingesting contaminated foods or drinks (considered one of the causes of food poisoning). And it is usually associated with:
- Yellow diarrhea, jaundice.
- Low-grade fever.
- Abdominal colics.
- Nausea and vomiting.
If you have jaundice or you suspect hepatitis A virus infection, consult your doctor immediately.
2- Recurrent attacks of Yellow diarrhea.
A- Irritable Bowel syndrome.
Irritable bowel syndrome is a very common medical condition that affects 10-15% of people worldwide. A large subset of IBS patients may have IBS-predominant diarrhea [ref].
It is OK for you if you are an IBS sufferer to experience yellow diarrhea during IBS flare-ups. No need to worry about your IBS yellow diarrhea as long as it comes and goes without any warning signs.
To have IBS, you must experience Recurrent abdominal pain at least one day per week for the last three months with symptoms onset more than six months.
Your IBS may be diarrhea-predominant, constipation-predominant, mixed, or unspecified type. If are already have IBS with diarrhea or mixed type, you may experience watery diarrhea now and then and it is normal with your IBS.
But if you experience recurrent attacks of yellow diarrhea and you suspect IBS, you should consult your doctor to confirm the diagnosis of your IBS, and until this happens, you can learn about How is IBS diagnosed in this interesting article.
B- Food allergy/food intolerance.
Food allergy and food intolerance are very common conditions and are overlooked by many doctors and patients. A large subset of people diagnosed with IBS may have underlying food intolerance causing their IBS-like symptoms.
The most common symptoms of food intolerance are diarrhea, with can be yellow diarrhea. In the table below, you can learn the difference between food intolerance and food allergy.
Food intolerance | Food allergy |
Affects 15-20% of the population | Affects nearly 2-5% of adults |
Difficulty digesting certain types of food (not immune-mediated allergy). | An immune-mediated reaction to certain foods or food components. |
Causes “recurrent acute” or “chronic” attacks of diarrhea (which can be yellow diarrhea). | Usually causes acute attacks related to the ingestion of offending food. It also can cause yellow diarrhea. |
Intestinal symptoms: diarrhea, extensive gas, bloating, and abdominal pain | Intestinal symptoms are the same |
No extra-intestinal symptoms | Extraintestinal symptoms like rashes, urticaria, swollen lips or face or severe life-threatening allergic reactions. |
The severity of your symptoms is proportional to the amount you eat from the offending food. | Even trace amounts of the offending food can produce severe symptoms. |
Common offending foods:
| Common offending foods: (examples)
|
3- Causes of chronic Yellow diarrhea.
If you came here searching for a cause of your yellow stool, you are mostly experiencing either acute or recurrent attacks. However, yellow diarrhea can be chronic. This “chronic” form of yellow diarrhea is usually due to chronic disease or organ malfunction.
And it will always be associated with more significant symptoms such as Jaundice, chronic abdominal pain, or a history of gallbladder stones.
The causes enlisted here cause chronic yellow diarrhea. if you already know you have any of the below conditions, then it will be the cause of your yellow diarrhea.
A- Gallbladder diseases/Stones:
Many gallbladder conditions can lead to yellow diarrhea, such as:
- Noncalcular Cholecystitis: inflammation of your gallbladder without stones inside it.
- Calcular Cholecystitis: inflammation due to gallstones?
- Gallbladder sludge
- Gall bladder removal.
- Other rare gallbladder diseases such as biliary atresia and primary biliary cholangitis.
Symptoms suggesting gallbladder disease:
- Pain in the upper right quadrant of your abdomen.
- Chronic or recurrent attacks of yellow diarrhea or greasy stools (especially occur after the ingestion of high-fat meals)
- Nausea or vomiting.
If you had your gallbladder removed, you might experience some yellow diarrhea. But if you don’t know if you have any gallbladder problems or not, please consult your doctor, especially if you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above.
The key to avoiding gallbladder/post-cholecystectomy yellow diarrhea is to avoid fatty meals.
B- Celiac Disease.
The typical form of celiac disease is severe chronic diarrhea associated with anemia and weight loss. It is due to sensitivity to a protein called “gluten” present in wheat and barley.
Usually, it presents in early childhood, with chronic severe diarrhea (which can be yellow) related to wheat-based foods.
The main treatment relies on cutting all gluten from food and eating a gluten-free diet.
Learn more about celiac disease.
C- Inflammatory Bowel disease (Crohn’s and Ulcerative Colitis).
Also, this disorder doesn’t cause simple yellow diarrhea, as the condition is more chronic and severe and may be associated with Mucus and blood in the stool, severe abdominal pain, and weight loss.
Learn more about Inflammatory bowel disease.
D- Bile Acid Diarrhea.
Another underestimated medical condition is associated with defective bile reabsorption by your intestines. The bile secreted into your intestine remains inside and traps water and leads to chronic yellow diarrhea.
Symptoms:
- Yellow/Golden diarrhea: especially after eating fatty meals.
- Severe Urgency to poop: This may lead to stool leakage, especially in older ages.
- More frequent in obese people.
- Bloating and indigestion are present in many people with BAD (Bile Acid Diarrhea).
Bile acid diarrhea is a chronic condition requiring your doctor’s intervention to diagnose and treat it reliably.
MORE:
- 10 Causes of Light Brown Stools: What’s Normal & Not?
- Why is your Stool Never Solid anymore? 7 Causes of Chronic Loose Stool.
FAQs:
Why is my poop yellow and mucusy?
A yellow, mucus-laden stool can be a result of various factors. The presence of mucus in stool is typically a sign that your intestines are producing more mucus than usual, which can happen when there’s an infection, inflammation, or other irritations. The yellow color might be due to the rapid transit of stool through the intestines, certain foods, or a lack of bile salts. Conditions like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), infections, or certain dietary choices can lead to these symptoms. If this persists or is accompanied by other symptoms, consulting a physician is essential.
Does yellow diarrhea mean liver damage?
Yellow diarrhea doesn’t directly indicate liver damage. However, the liver produces bile, which helps in the digestion of fats. If the liver is damaged, it might not produce enough bile, leading to stool that can appear pale or clay-colored. Yellow diarrhea, on the other hand, is often due to the rapid transit of stool through the intestines or an issue with fat digestion. While yellow diarrhea alone isn’t a direct sign of liver damage, if you’re experiencing other symptoms like jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), it’s crucial to seek medical attention.
What causes yellow diarrhea that smells like rotten eggs?
A foul-smelling, yellow diarrhea that resembles rotten eggs is often due to the presence of hydrogen sulfide gas produced by bacteria in the colon. This can be caused by the consumption of certain foods high in sulfur, such as eggs, meat, and certain vegetables. Additionally, infections like giardiasis or conditions like malabsorption can lead to this symptom. The presence of undigested fats in the stool can also contribute to the foul odor.
Is yellow a symptom of a bile leak?
Yellow isn’t directly a symptom of a bile leak. However, bile is a yellow-green fluid produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder. If there’s a bile leak, it might lead to symptoms like abdominal pain, fever, or jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes). The stool might appear pale or clay-colored due to a lack of bile in the intestines rather than yellow. If you suspect a bile leak or experience any associated symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical attention immediately.
- Evidence-based
- Written by a doctor.