Bright Yellow Watery Diarrhea: 6 Causes
- Bright yellow can be the normal color of severe watery diarrhea. This is due to the speed of stool passing inside your intestine before it acquires its brown color.
- Infections with gut viruses, protozoa, or bacteria are the most common cause of acute bright yellow watery diarrhea.
- The most common organisms are norovirus, rotavirus, and giardiasis.
- Causes of recurrent, intermittent, or chronic bright yellow watery diarrhea include chronic infections, food intolerance, irritable bowel syndrome, and drug-induced diarrhea.
How does your stool Become bright yellow (and watery)?
More than one mechanism can aid in the transformation of your stool into a bright yellow color, most commonly:
- Speeding up of stool passage: To acquire its brown color, your stool must have enough time to stay inside your colon to be processed to its brown color. Any process of “speeding up” poop passage through your colon can cause its color to become yellow. So, any form of severe diarrhea can lead to a bright yellow color of your diarrhea. Examples:
- Infections (Gastroenteritis): especially the watery, non-inflammatory type
- IBS with predominant diarrhea.
- Laxative abuse.
- Presence of more fat in your stool: any condition that leads to fat malabsorption or fat overload. More fat in your stool leads to yellow or yellowish-grey color (greasy). Examples:
- Pancreatic diseases lead to fat malabsorption.
- Gallbladder diseases lead to fat malabsorption.
- Bile acid diarrhea (Malabsorption).
- Giardiasis: a common infection that affects fat absorption and causes bright yellow watery diarrhea.
- Other factors contributing to bright yellow diarrhea:
- High bilirubin, as with Gilbert’s syndrome, affects about 3% of people worldwide.
- Certain foods may cause bright yellow stools, such as carrots, sweet potatoes, turmeric, and high-fat foods.
Before you start reading about what caused your bright yellow diarrhea, there are some things to put into consideration:
- Duration of your yellow watery diarrhea:
- Hours to a few days (acute diarrhea): diarrhea lasting up to 2 weeks is called acute diarrhea. The most common causes are infection (gastroenteritis). Less common causes include drugs such as laxative abuse and antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
- Diarrhea in intermittent attacks (flare-ups and remissions) for extended periods (months or years): most commonly occurs due to irritable bowel syndrome. Other causes include alcohol abuse, lactose intolerance, and other food intolerance.
- Continuous yellow watery diarrhea for more than four weeks: is usually due to chronic gut conditions such as celiac disease and chronic infections, especially in people with chronic conditions such as HIV, Diabetes. Also, with inflammatory bowel disease and malabsorption syndromes.
- Presence of warning signs:
- High-grade fever.
- Severe or persistent vomiting.
- Reddish or blackish stool (blood in stool).
- Intolerable abdominal pain and tenderness.
- Pus-filled stool.
- Inability to urinate, difficulty breathing, confusion, severe dizziness, or loss of consciousness (signs of severe dehydration).
- Diarrhea not responding to usual treatments or prolonged more than three days.
RELATED: How To Treat Yellow Stool.
1- Infections: (the most common cause of ACUTE yellow watery diarrhea)
The most common cause of acute onset bright watery yellow diarrhea is infections. The infection of your gut can be due to the following:
- viruses (most common cause),
- bacteria.
- parasites (giardiasis, in particular, causes bright watery yellow stool),

You get infections by:
- Eating contaminated foods or drinks,
- Traveling to endemic areas, or
- Contacting an infected person.
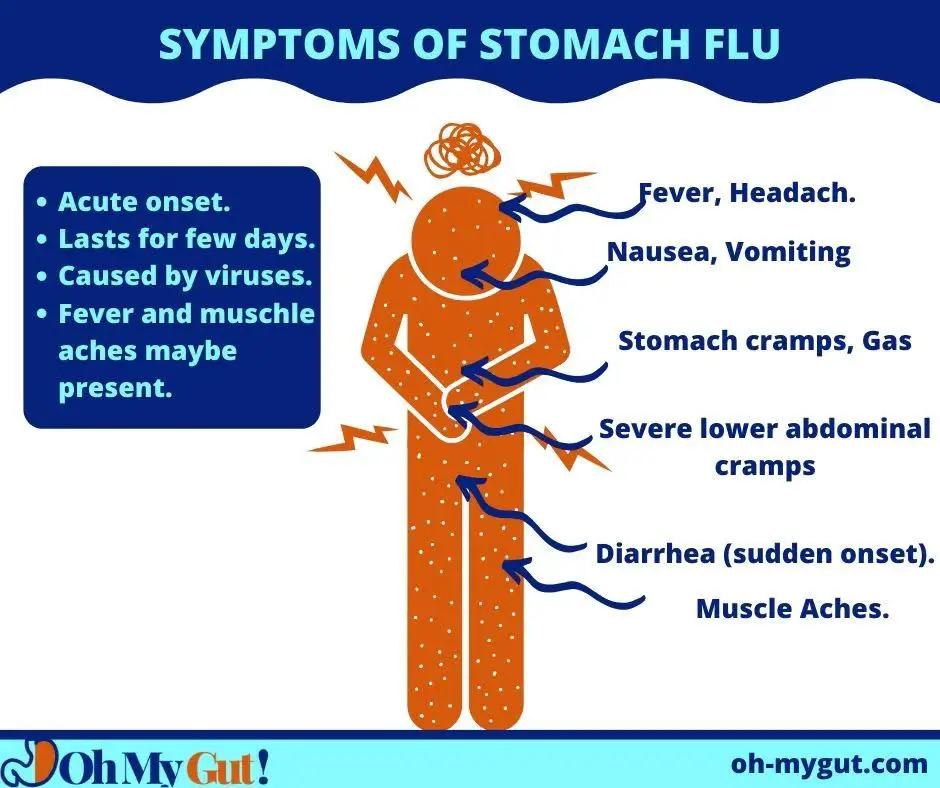
[1-A] viral diarrhea (Stomach flu) (acute bright yellow water diarrhea).
If you have bright yellow watery diarrhea of acute onset, the most common cause is viral gastroenteritis (stomach flu). (reference)
The most common viruses causing yellow watery diarrhea are rotavirus and Norwalk viruses. Rotavirus is considered the most common cause of diarrhea worldwide (reference). Recently, Norovirus (Norwalk virus) became the most prevalent cause after introducing the Rotavirus vaccine.
Symptoms suggesting viral diarrhea:
- Light brown to bright yellow watery diarrhea.
- Abdominal cramps and pain.
- May be: loss of appetite, nausea, and/or vomiting
- Fever, usually low grade.
- Maybe muscle aches or headache
- It lasts for hours to a few days.
- NOT associated with bloody stools or high-grade fever.
- Complications commonly occur in young children or older ages. It includes dehydration, nutritional imbalances, and weakness.
How to deal with:
- It is usually a mild and self-limiting disease.
- Drink plenty of fluid.
- Eat small frequent meals.
- Try to eat bland foods (BRAT food) such as rice, toast, applesauce, potatoes, and bananas.
- Avoid foods causing stomach upset, such as fatty foods, caffeine, sugary foods, and dairy.
- Currently, No antiviral medicines can kill gut viruses. So, there is no need for medications (self-limiting conditions) unless prescribed by your doctor.
When to see a doctor:
- Severe diarrhea with several attacks or persistent vomiting.
- High-grade fever.
- Bloody diarrhea.
- If you have other chronic illnesses such as HIV or diabetes.
- Signs of dehydration like confusion, lethargy, dry mouth, decreased urine, or dark yellow.
- Age extremes with severe diarrhea in young infants and elderly over 70 years of age.
RELATED: How To Treat Yellow Stool.
Can Yellow Diarrhea Be a Symptom of COVID-19?
Protozoa: Especially giardiasis
Giardia is a protozoan that is famous for causing bright yellow watery diarrhea. According to the CDC, Giardiasis is the most common protozoan causing diarrhea in the US.
Giardiasis is caused by ingesting contaminated food or water and fecal-oral infection. For example, traveling to areas with poor sanitary conditions.
It commonly causes Fat Malabsorption. And this is the cause of bright yellow watery, or greasy diarrhea.
Common protozoa causing bright yellow watery diarrhea include cryptosporidium parvum (in vegetables, fruit, and unpasteurized milk). Also, Cyclospora Cayetanensis (in imported berries and herbs) can cause diarrhea, especially in advanced HIV patients. (reference)
Symptoms (how to suspect?): (reference)
- Diarrhea: bright yellow or fatty stools, foul-smelling: in 90% of symptomatic giardiasis.
- Malaise (feeling ill or discomfort): prevalent in 86% of cases.
- Abdominal cramps and bloating. Flatulence also occurs.
- Nausea (69%) or vomiting (23%).
- Weight loss is common (66%).
- Fever is rare (only in 15% of cases).
- Traveling to areas with bad sanitary conditions in the past one or two weeks.
- Giardiasis can become chronic. It causes loose stools (not diarrhea), malabsorption, profound weight loss, fatigue, and depression.
- High-risk groups: infants, young children, and travelers (reference)
How to deal?
- If you suspect that your bright yellow diarrhea is caused by giardiasis, consult your doctor for treatment.
- Treatment options include:
- Metronidazole for 5-7 days, but it causes nausea and a metallic taste.
- Nitazoxanide for three days (also available as a syrup for children).
- Tinidazole is as effective as metronidazole, known as a single dose.
- Stick to the standard advice for diarrhea: plenty of fluid, a BRAT diet, and avoid diets triggering diarrhea, such as alcohol and caffeine.
Bacterial diarrhea (the non-inflammatory type):
Some bacteria cause severe diarrhea (inflammatory diarrhea) with fever and blood in stools. Others may cause simple bright yellow watery diarrhea (non-inflammatory diarrhea).
The most common bacteria causing watery yellow diarrhea (non-inflammatory type) :
- Clostridium difficile: common infection, especially after antibiotic use, taking drugs that suppress gastric acidity, and with cancer chemotherapy.
- Clostridium perfringens: usually acquired by eating undercooked meat, poultry, or home-canned goods.
- Listeria monocytogenes: another bacteria acquired from processed meat, hot dogs, soft cheese, and pâtés. It affects special groups such as pregnant women, very young and elderly, and people with impaired immunity.
Other bacterial types cause a more severe form of diarrhea (inflammatory diarrhea) with high-grade fever, bloody stools, and not-yellow watery diarrhea.
2- Food intolerance/allergy.
Food intolerance is widespread, affecting up to 20% of people. It can lead to severe diarrhea in some instances. The severe diarrhea is usually yellowish and may be watery. Also, food allergies can cause the same. See the difference below.
| Food intolerance | Food allergy |
| Affects 15-20% of the population | Affects nearly 2-5% of adults |
| Difficulty digesting certain types of food (not immune-mediated allergy). | An immune-mediated reaction to certain foods or food components. |
| Causes “recurrent acute” or “chronic” attacks of diarrhea (which can be bright yellow & watery). | Usually causes acute attacks related to the ingestion of offending food. |
| Intestinal symptoms: diarrhea, extensive gas, bloating, and abdominal pain | Intestinal symptoms are the same |
| No extraintestinal symptoms | Extraintestinal symptoms like rashes, urticaria, swollen lips or face, or severe life-threatening allergic reactions. |
| The severity of your symptoms is proportional to the amount you eat from the offending food. | Even trace amounts of the offending food can produce severe symptoms. |
| Common offending foods:
| Common offending foods: (examples)
|
3- Drinking alcohol (even small amounts)
alcohol speeds up things inside your intestine and colon. This can cause bright yellow watery diarrhea. Even if you drink small doses, it is worse to mention that it can cause diarrhea. Alcohol can irritate your digestive tract and worsen existing diarrhea. (ref)
Also, chronic use of alcohol can cause liver and pancreatic problems (such as chronic pancreatitis), causing maldigestion and malabsorption of fat, leading to chronic yellow diarrhea.
4- Irritable bowel syndrome.
Irritable bowel syndrome is another common underdiagnosed disease. It affects nearly 20 to 15% of the population.
Irritable bowel syndrome is characterized by chronic abdominal pain or cramps related to defecation, change in stool frequency, or change in stool form.
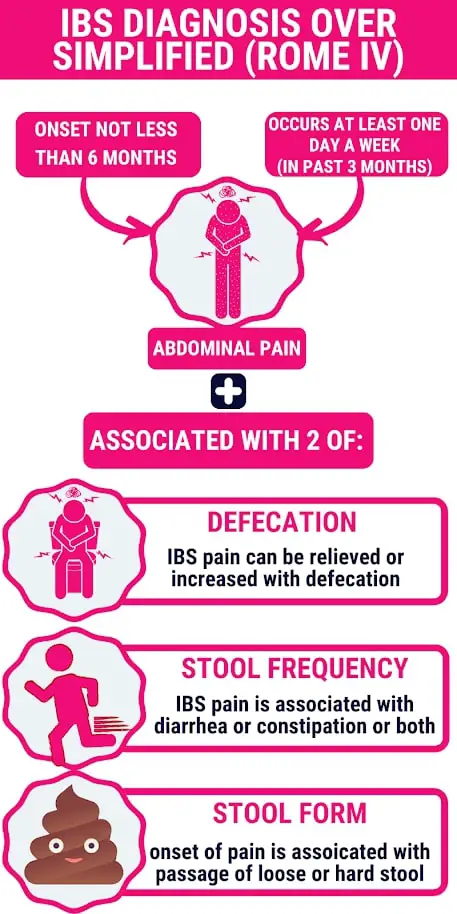
IBS has four types: IBS-Diarrhea predominant, IBS-Constipation predominant, IBS-Mixed type, and IBS-Unclassified.
With IBS (especially the diarrhea-predominant type), it is common to experience bright yellow stool with IBS. as an IBS flare-up with yellow diarrhea.
Food triggers such as FODMAPs and alcohol can worsen your IBS and cause bright yellow watery diarrhea.
Suspect IBS if you have recurrent abdominal cramps (at least once per week) for the past three months associated with defecation or stool changes.
To learn more, see how IBS is diagnosed.
It is worth mentioning that stress and anxiety can trigger IBS. If you always get bright yellow watery diarrhea in stressful conditions, you must suspect IBS.
This study illustrates that stress and anxiety are far more common among people with IBS.
5- Drugs that cause yellow & watery diarrhea.
More than 700 drugs are linked to diarrhea (reference). Diarrhea can be watery and bright yellow or severe with bloody stool. The most common causes of watery yellow diarrhea are laxative abuse and antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
A] Laxative abuse:
Laxative causes watery yellow diarrhea either by increasing motility (contractions) of your intestine or by drawing water into your gut.
Also, magnesium-containing laxatives or supplements can have laxative effects and cause diarrhea.
Abuse or large doses of laxatives can be problematic.
Common laxative causing watery diarrhea:
- Senna.
- Docusate sodium.
- Magnesium oral solution and magnesium-containing antacids.
Please stop the laxative if you get bright yellow water diarrhea after using a laxative or an antacid for heartburn. Contact your doctor if diarrhea doesn’t improve.
Learn more about laxative abuse.
B] Antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
Diarrhea that occurs after taking antibiotics to treat any bacterial infection is called antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea can range from mild self-limiting loose stool or diarrhea (watery and bright yellow) to severe forms with bloody diarrhea (severe colitis).
Common antibiotics causing diarrhea:
- Penicillins such as ampicillin and amoxicillin.
- Clindamycin
- Cephalosporins: such as cefpodoxime cephalexin.
Suspect antibiotic-associated diarrhea if:
- The onset of diarrhea after taking antibiotics.
- Symptoms other than diarrhea include crampy abdominal pain, fever, and tenderness.
- Have a history of antibiotic-associated diarrhea before.
- Using more than one antibiotic at the same time.
- Taking antibiotics for long periods.
C] Other drugs causing yellow or watery diarrhea.
Many drugs other than laxatives and antibiotics can cause yellow or watery diarrhea. The most common types include:
- Metformin: a common anti-diabetic drug.
- Chemotherapy: in people with cancer.
- Immunosuppressive drugs: such as mycophenolate. Used in people with immunological diseases such as systemic lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, and others.
- Drugs used to treat heartburn, GERD, and gastritis (proton pump inhibitors and H2 blockers): as esomeprazole (Nexium ®), Pantoprazole (Protonix ®), Omeprazole (Prilosec ®), and ranitidine (Zantac ®).
This is NOT a complete list of drugs causing diarrhea. Learn more here and here.
Contact your doctor to evaluate if it is necessary to stop the antibiotic and if there is any treatment for your diarrhea.
6- Other medical conditions (rare, chronic, associated with other symptoms).
All the below conditions can cause bright yellow watery diarrhea. But it is relatively rare and usually associated with other prominent symptoms. Also, diarrhea from these conditions is always prolonged or recurrent over long periods.
Inflammatory bowel disease:
Inflammatory bowel disorders include Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. The condition is usually more severe, and diarrhea is prolonged. You may find blood or mucus with diarrhea. Also, weight loss and fever may occur.
Gallbladder diseases.
Inflammation (cholecystitis) or gallbladder removal can lead to bright yellow watery diarrhea, especially after eating fatty foods.
Celiac disease.
Celiac disease occurs due to intolerance to gluten protein present in wheat and barley. Usually, it is a chronic condition associated with watery diarrhea and malabsorption related to the ingestion of wheat-based foods. In addition, it can be related to anemia, weight loss, and abdominal pain.
Bile acid diarrhea:
Another less common condition can lead to bright yellow water diarrhea. With bile acid diarrhea, the following occurs: (reference)
- Your intestine cannot usually reabsorb or handle the bile secreted by your liver and gallbladder.
- Bile acid inside your intestine and colon traps water and causes bright yellow water diarrhea.
Suspect bile acid diarrhea if you have:
- Diarrhea: after eating fatty foods or even chronic diarrhea at any time (not only after meals).
- A unique feature of diarrhea is that you may have severe urgency, and the risk of stool leakage may occur, especially at older ages.
- It is usually watery diarrhea, more frequent in obese people.
- Bloating and indigestion may be present.
FAQs About Bright Yellow Watery Diarrhea:
What are the most common causes of yellow watery diarrhea in adults?
The most common cause of yellow watery diarrhea in adults are infections, including viral gastroenteritis (acute form), and irritable bowel syndrome (chronic or recurrent form).
What Causes Neon (highlighter) yellow watery diarrhea?
Neon watery yellow diarrhea is often caused by infections such as viral gastroenteritis and giardiasis. Other causes include fat intolerance, irritable bowel syndrome, and bile acid diarrhea.
What are the commonest causes of explosive yellow diarrhea?
Acute explosive diarrhea is typically due to infections (gastroenteritis), whether it is viral (such as norovirus), bacterial, or protozoal (particularly giardiasis). Recurrent explosive yellow diarrhea are occurs commonly due to irritable bowel syndrome, food intolerances (such as lactose intolerance), and bile acid diarrhea.